Storage Setup
You store the gateway data on volumes. You can create arrays to combine multiple disk drives and then create volumes or create volumes per disk.
Using Arrays to Combine Drives
Arrays combine multiple drives. There are several types of arrays which can provide any and all of the following benefits:
Note: The H-Series and X-Series of Edge Filers are supplied with arrays that are preconfigured. These arrays cannot be changed.
Which is the Right Type of Array
How many hard drives do you have installed in your gateway? Do you want every drive to be redundant in case of failure, or do you want to use the maximum amount of storage space you can? And how does the array type affect the performance?
To combine the capacity from two or more drives, you can create a JBOD (Just a Bunch of Disks) array. This type of array lets you use a set of drives like one drive. For example, one 500 GB drive and one 950 GB drive in such an array would act as a 1450 GB drive. You can then create volumes of any size on the array adding up to a total of 1450 GB. Virtual Gateways can only be configured with JBOD Arrays.
If you have two or more drives and you want to maximize your drive speed, you can create a RAID0 array. In RAID0, data is striped across all the drives in the array. A RAIDO array acts as one drive with the combined capacity of all the drives in the array and faster performance.
For full redundancy, you can create a RAID1 array from two or more disks. RAID1 mirrors (duplicates) all data across all drives in the array. Data is only lost if all drives in the array fail. Since the exact same data must be written on each disk in the array, the capacity of a RAID1 is the capacity of the smallest drive in the array.
If you have three or more drives, you can have redundancy with a RAID5 array. RAID5 uses striping and distributed parity. Data is striped onto the drives and parity information is distributed across all the disks. If one drive fails, the data can be reconstructed from the parity information. The capacity of a RAID5 array is (n-1)*s, where n is the number of drives and s is the size of the smallest drive.
If you have more than three drives, you can create a RAID6 array, which uses dual parity with striping. That means maximized speed and the data is safe even if two drives fail. The capacity of a RAID6 array is (n-2)*s, where n is the number of drives and s is the size of the smallest drive.
What is Striping
In striping, data is chopped up into data blocks, smaller pieces of data, and blocks are written to all the drives in the array instead of all the data being written to one drive. This means the writing is done in parallel and the performance is increased. When the data is read from the drives, for restore, backup or sync operations, the performance is also faster.
Which Arrays are Supported
Can I hot swap drives from an array (C-Series Gateways Only)?
RAID1, 5, and 6 support hot swapping, in which drives are replaced without turning off the gateway. The array remains accessible throughout the hot swap procedure. For further information, see the CTERA Edge Filer (Gateway) Installation and Maintenance Guide for your Edge Filer.
Using the Storage Setup Wizard
You can use the Storage Setup Wizard in either the Arrays or Volumes pages, to detect the drives in your gateway and create and array and one logical volume on the array using the whole capacity of the array. The wizard is displayed automatically upon initial login; however, if desired, you can close the wizard at any stage, and set up the gateway without the aid of the wizard.
Alternatively, you can create the arrays and volumes with full control of what you want to create. If you want to create a RAID0 array, use the procedure described in Managing Arrays.
To setup the gateway storage using the Storage Setup Wizard:
1 In the CONFIGURATION tab, select Storage > Arrays or Storage > Volumes in the navigation pane and click Storage Setup Wizard.
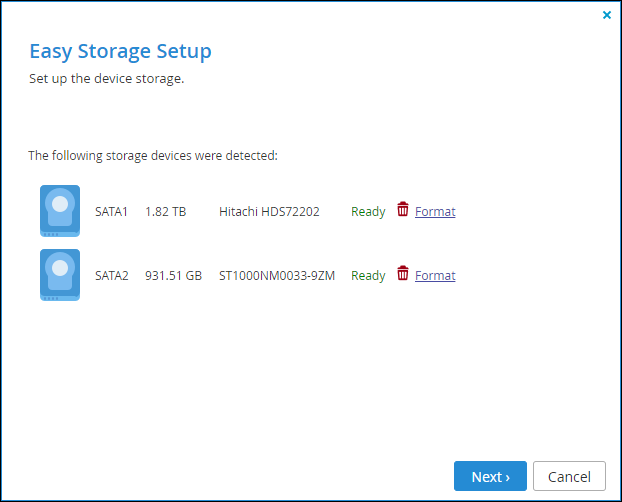
A Format link is displayed if there is data on the drive. If there is no data on the drive, the drive's status is Empty and the drive is formatted automatically. Clicking Format and then Yes to confirm, formats the drive and erases all the data on the drive.
Warning: Formatting erases all data on the drive.
2 Click Next.
If the Storage Setup Wizard determines that certain storage configuration changes involving this drive would be beneficial, the Proposed Actions window is displayed describing the changes.
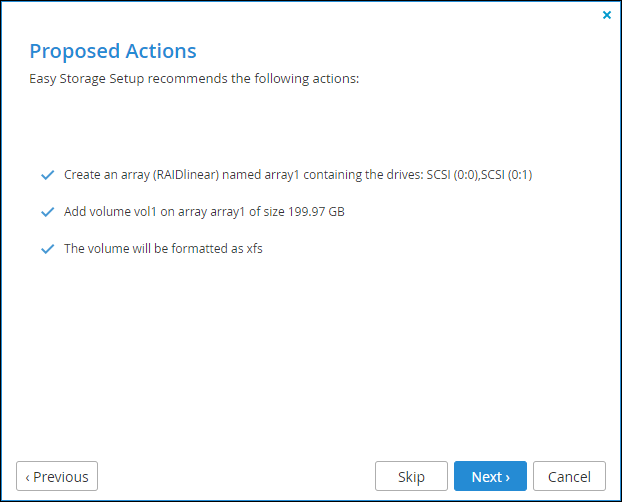
3 Select one of the options, click Next.
On the first time the wizard runs, the following backup encryption window is displayed.
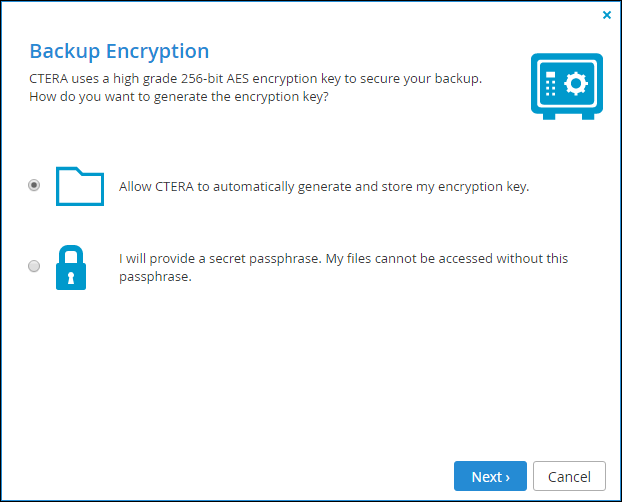
4 Select the encryption you require. If you want to use a passphrase to protect your data, you specify the passphrase and then confirm this passphrase by retyping it.
Volume encryption is supported both for standalone volumes and volumes residing in RAID arrays. The encryption method employed is the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES-256 CBC ESSIV). Enabling volume encryption may reduce performance.
Note: It is important to keep the passphrase in a safe place, as there is no way of retrieving it if you lose it. If you reset your gateway to its default settings, you cannot access the volume without this passphrase.
5 Click Next and then click Finish in the Wizard Completed screen.